As stated by their name, unchecked exceptions are not checked at compile-time which means that the compiler doesn’t require methods to catch or to specify (with a throws) them. Classes belonging to this category are detailed in the section 11.2 Compile-Time Checking of Exceptions of the JLS:
The unchecked exceptions classes are the class
RuntimeExceptionand its subclasses, and the classErrorand its subclasses. All other exception classes are checked exception classes. The Java API defines a number of exception classes, both checked and unchecked. Additional exception classes, both checked and unchecked, may be declared by programmers. See §11.5 for a description of the exception class hierarchy and some of the exception classes defined by the Java API and Java virtual machine.
The following picture illustrates the Exception hierarchy:
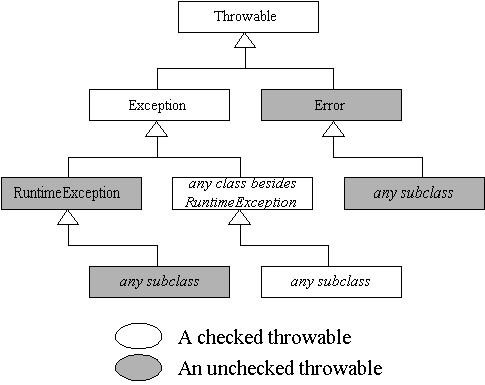
The class Error and its subclasses are exceptions from which ordinary programs are not ordinarily expected to recover and, as explained in 11.5 The Exception Hierarchy:
The class
Erroris a separate
subclass ofThrowable, distinct from
Exceptionin the class hierarchy, to
allow programs to use the idiom:} catch (Exception e) {to catch all exceptions from which
recovery may be possible without
catching errors from which recovery is
typically not possible.
To summarize, RuntimeException are a subset of unchecked exceptions for exceptions from which recovery is possible (but unchecked exception is not a synonym of RuntimeException as many are answering here).